Introduction
Septic tanks are an essential part of many residential and commercial properties’ wastewater management systems. These underground structures play a crucial role in treating and disposing of household or business sewage. Understanding their lifespan is critical for ensuring functionality and avoiding potential problems. In this article, we will delve into the factors influencing the lifespan of septic tanks, discuss signs of decay, and offer useful tips for prolonging their longevity.
I. Purpose of a Septic Tank
A. Explanation of how septic tanks function
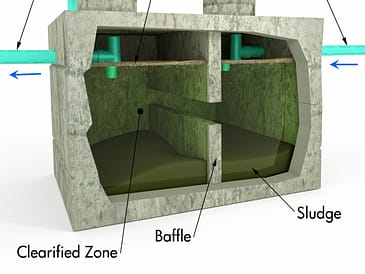
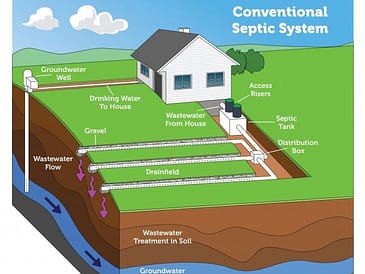
Septic tanks work through a natural and passive process. They separate solid waste from liquid waste and gradually break down the waste materials through the activity of bacteria present in the tank. The liquid effluent is eventually released into a drain field or leach field, where it gets further treated by the surrounding soil.
B. Role of bacteria in the tank
The bacteria present in the septic tank play a vital role in the decomposition process. Anaerobic bacteria primarily break down the solid waste, converting it into gases and sludge. The effluent passes through a series of treatment stages within the septic system and is gradually purified by the bacterial action, resulting in cleaner water that is suitable for natural absorption into the groundwater.
II. Factors Affecting the Lifespan of Septic Tanks
A. Quality and design of the tank
The quality and design of the septic tank itself significantly impact its lifespan. Tanks made from durable materials such as concrete or fiberglass tend to last longer than those made from low-quality materials. Additionally, proper design considerations, such as size, baffles, and compartmentalization, can enhance the tank’s performance and longevity.
B. Proper installation and maintenance
The correct installation of a septic tank by experienced professionals is crucial to ensuring its longevity. Improper installation, such as inadequate depth or incorrect positioning, can lead to a shorter lifespan and potential issues. Regular maintenance, including pumping out the tank when necessary, inspections, and addressing any repairs promptly, is vital for keeping the system running smoothly.
C. Soil conditions
The quality and composition of the surrounding soil have a direct impact on the septic tank’s lifespan. Soil with good drainage capabilities facilitates the efficient leaching of effluent, reducing strain on the system. Conversely, soil with high clay content or poor drainage can lead to clogging and premature failure of the septic tank.
D. Water usage and household size
Excessive water usage or a large number of occupants in a property can put additional strain on a septic tank. The more wastewater generated, the more the septic system must work, potentially leading to earlier wear and tear. Conserving water and practicing water-saving habits can help prolong the life of the septic tank.
III. Typical Lifespan of Septic Tanks
A. Range of lifespan based on various factors
The average lifespan of a well-maintained septic tank can vary depending on several factors. Generally, a concrete septic tank can last anywhere from 20 to 40 years, while a fiberglass tank has a lifespan of 30 to 50 years. These estimates are rough guidelines, as numerous factors affect the actual longevity.
B. Factors affecting the lifespan
The factors discussed in the previous section, including tank quality, installation, maintenance, soil conditions, and water usage, significantly influence the lifespan of a septic tank. Neglecting any of these factors can decrease the tank’s lifespan and potentially lead to expensive repairs or replacements.
C. Signs of a failing septic tank
Recognizing the signs of a failing septic tank is crucial for taking appropriate action before the problem escalates. Common signs include foul odors, slow-draining sinks and toilets, sewage backups, unusually lush patches of grass or vegetation over the drain field, or greener grass around the tank area. Immediate attention is necessary to prevent further damage to the tank or contamination of the surrounding area.
IV. Prolonging the Lifespan of Septic Tanks
A. Regular maintenance and inspections
Scheduled pumping and regular inspections help ensure the proper functioning of a septic tank. Pumping out the tank at recommended intervals removes accumulated sludge and prevents it from affecting the performance and lifespan of the septic system. Inspections can identify potential issues early on, allowing for timely repairs or adjustments.
B. Proper usage and disposal practices
Educating household members or property occupants about responsible water usage practices can significantly impact the lifespan of a septic tank. Encouraging the use of low-flow fixtures, spreading laundry loads over multiple days, and avoiding excessive water usage during peak times can reduce strain on the system. Additionally, educating on proper waste disposal, such as avoiding flushing non-biodegradable items, helps prevent tank clogging and extends its lifespan.
C. Monitoring water usage and reducing waste
Installing water meters or using water usage tracking systems can help monitor water consumption, enabling households or businesses to identify areas where further reduction is possible. Water-saving habits, such as fixing leaky faucets or toilets promptly and following proper laundry and dishwashing practices, contribute to preserving the lifespan of the septic tank.
V. Replacement and Expenses
A. Factors to consider when replacing a septic tank
When a septic tank reaches the end of its lifespan or develops irreparable issues, replacement becomes necessary. Several factors play a role in determining the replacement process, including soil conditions, tank size, location, and local regulations or permits.
B. Potential costs associated with replacement
Replacing a septic tank can be a significant expense for property owners. The cost depends on various factors, including the tank material, excavation requirements, additional plumbing modifications, and any required permits. Seeking quotes from reputable professionals and comparing options can help manage the expenses.
VI. Environmental Considerations
A. Impact of failing septic tanks on groundwater and the surrounding environment
A failing septic tank can release untreated or partially treated effluent into the groundwater, posing risks to human health and the environment. Harmful pathogens, nitrates, and other contaminants can contaminate nearby wells, rivers, streams, or surface water, leading to pollution and potential health hazards. Regular maintenance and promptly addressing septic tank issues minimize the environmental impact.
B. Importance of timely repairs or replacements
Timely repairs or replacements are essential for mitigating the negative environmental consequences of a failing septic tank. Ignoring or neglecting septic issues can result in significant pollution and costly cleanup efforts. Responsible septic tank ownership includes maintaining the system’s reliability to protect both the property owner and the surrounding ecosystem.
Conclusion
Understanding the lifespan of septic tanks is crucial for property owners seeking to maximize their investment and protect the environment. Proper installation, regular maintenance, and responsible usage practices contribute to extending the life of septic tanks. Monitoring water usage, promptly addressing problems, and being mindful of environmental impacts ensure the longevity of septic systems. By taking these factors into account, property owners can enjoy the benefits of a functioning septic tank for many years while minimizing potential issues and expenses.