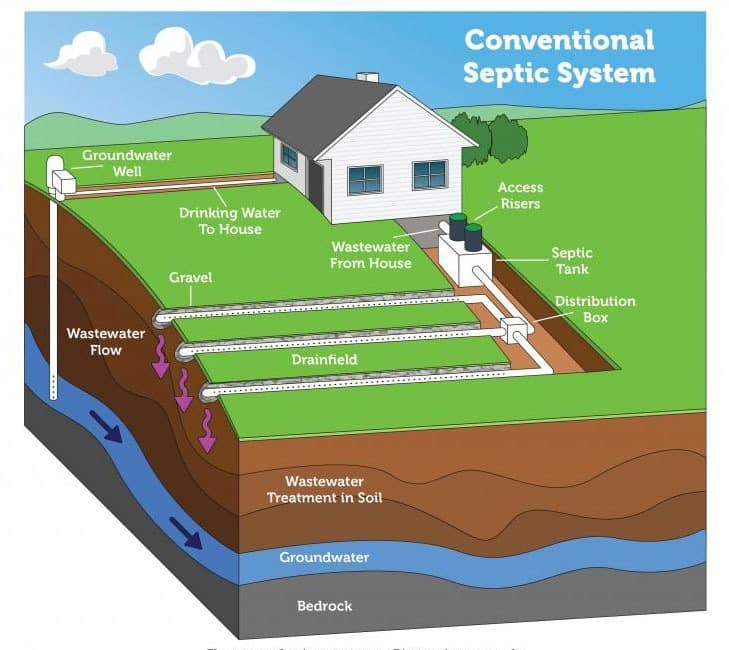
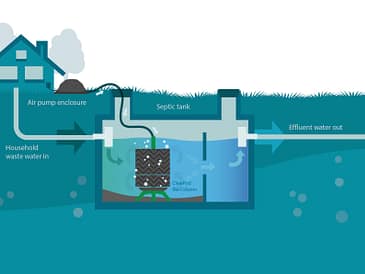
I. Introduction to Septic Tank Regulations in Oregon
Septic tank systems play a crucial role in managing wastewater in Oregon. These systems are designed to treat and dispose of household sewage when a home is not connected to a public sewer system. In order to ensure public health and protect the environment, the state of Oregon has implemented regulations for the proper management of septic tank systems.
Overview of septic tank systems
A septic tank system consists of a septic tank and a drain field. The septic tank is a large underground container that receives wastewater from the home. It separates solids from liquids and allows bacteria to break down the organic matter in the wastewater. The liquid portion, known as effluent, is then discharged into the drain field, where it is further filtered and treated by soil before reaching groundwater.
Importance of regulations for proper septic tank management
Regulations for septic tank systems are in place to protect public health and prevent contamination of groundwater, rivers, and lakes. When septic systems are not properly maintained or fail to meet required standards, they can pose serious risks to human health and the environment. These risks include the spread of diseases, pollution of water sources, and damage to ecosystems.
The Oregon Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ) is responsible for regulating septic tank systems. They establish rules and guidelines for the design, installation, operation, and maintenance of septic systems to ensure their proper functioning and prevent environmental harm.
Compliance with septic tank regulations is essential for anyone who owns or plans to install a septic system in Oregon. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in penalties, fines, and costly repairs. It is important to be aware of the specific requirements and procedures outlined by the DEQ, as they may vary depending on the location and characteristics of the septic system.
In conclusion, septic tank regulations in Oregon are crucial for the proper management of wastewater and the protection of public health and the environment. It is vital for homeowners and septic system operators to understand and comply with these regulations to ensure the safe and effective operation of their septic systems. Further information on septic tank regulations in Oregon can be found on the Oregon DEQ website here.
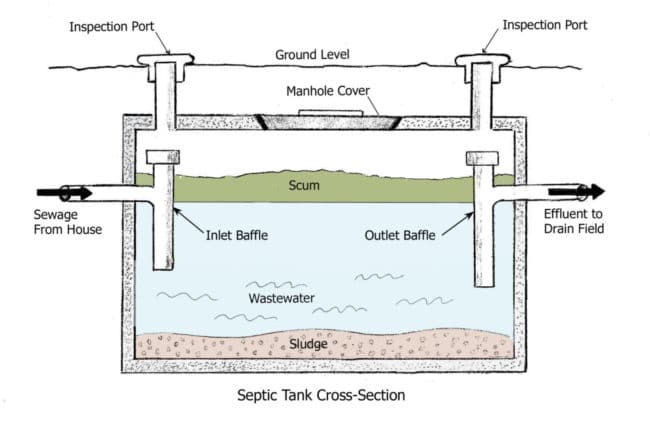
II. Oregon State Regulations for Septic Tanks
Oregon has specific regulations in place to ensure the proper installation and maintenance of septic tanks. These regulations are outlined in the Oregon Administrative Rules (OAR) and cover various aspects of septic tank systems. It is important for property owners to familiarize themselves with these regulations to avoid any fines or penalties and to ensure the safety and functionality of their septic systems.
Oregon Administrative Rules (OAR) related to septic tanks
The Oregon Administrative Rules (OAR) provide guidelines for the design, installation, operation, and maintenance of septic tanks. These rules are designed to protect the environment, public health, and groundwater quality. Some key provisions of the OAR related to septic tanks include:
- Tank Sizing and Design: The OAR specifies the minimum tank sizes and design requirements based on factors such as the number of bedrooms or occupancy of the property.
- Percolation Testing: Before installing a septic tank, a percolation test must be conducted to determine the soil’s ability to absorb and treat wastewater effectively. The OAR provides guidance on conducting this test and determining the appropriate size and type of septic system for the property.
- Installation and Permitting: The OAR outlines the requirements for obtaining a permit for septic tank installation. These requirements include submitting a detailed system design, obtaining the necessary approvals from local health authorities, and complying with setback distances from wells, property lines, and water bodies.
Permitting requirements for installation and maintenance
In Oregon, property owners must obtain a permit before installing or modifying a septic system. The permitting process ensures that the system meets the necessary standards and regulations. Some key permitting requirements include:
- Application: Property owners must submit a completed application form, along with detailed system plans, to the local health authority responsible for permitting septic systems.
- Inspections: Inspections are typically required at various stages of the installation process to ensure compliance with the approved system design. These inspections are conducted by qualified professionals designated by the local health authority.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance and inspections are also required for septic tanks to ensure their continued functionality and prevent any health or environmental issues. Property owners must adhere to the maintenance schedule outlined by the local health authority and keep accurate records of inspections and repairs.
It is essential for property owners in Oregon to be aware of these regulations and comply with them to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of their septic systems. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, penalties, and potential health and environmental hazards.
For more information on septic tank regulations in Oregon, you can refer to the Oregon Department of Environmental Quality’s website: https://www.oregon.gov/deq/wq/Pages/Onsite.aspx
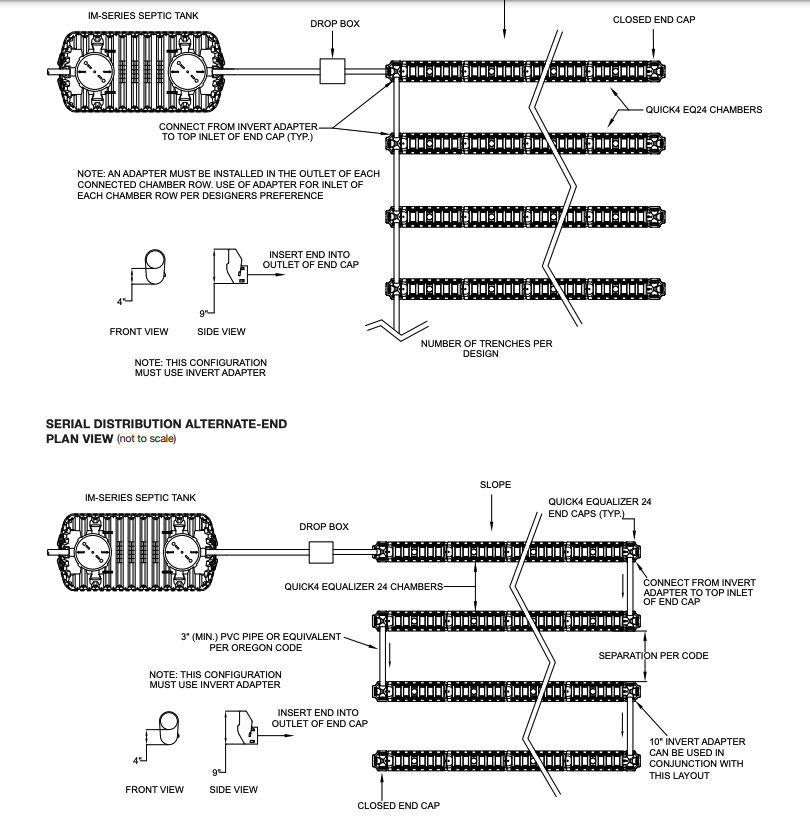
III. Septic Tank Design and Installation Standards in Oregon
When it comes to septic tank regulations in Oregon, there are specific minimum standards for design and construction that must be followed. These regulations are in place to ensure that septic systems are properly installed and maintained to protect public health and the environment. Here are some key points regarding septic tank design and installation standards in Oregon:
Minimum standards for septic tank design and construction
In Oregon, septic tanks must be designed and constructed in accordance with the state’s minimum standards. These standards dictate factors such as tank size, materials used, and installation practices to ensure proper functioning and longevity of the septic system. Some notable requirements include:
- Tanks must have a minimum liquid capacity of 1,000 gallons for residential use.
- Tanks must be made of watertight materials such as concrete or reinforced fiberglass.
- The lid of the septic tank must be secure and able to withstand a certain amount of weight.
- Tanks must be placed in a location accessible for maintenance and inspection.
Sizing requirements based on property size and soil conditions
When determining the size of a septic tank, property size and soil conditions play a crucial role. Oregon has guidelines that consider the number of bedrooms in a residence and the soil percolation rate. The percolation rate measures how quickly water can pass through the soil, indicating the level of treatment and absorption the septic system can provide. These guidelines ensure that the septic tank is appropriately sized to handle the expected wastewater load and prevent system failures and environmental contamination.
It is important to note that septic tank regulations may vary between counties within Oregon, so it is essential to check with the local health department or environmental agency for specific requirements in your area.
In conclusion, following the septic tank design and installation standards in Oregon is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of septic systems. Compliance with these regulations helps protect public health and the environment, preventing contamination of groundwater and surface water sources. For more detailed information on septic tank regulations, you can refer to the official guidelines provided by the Oregon Department of Environmental Quality.
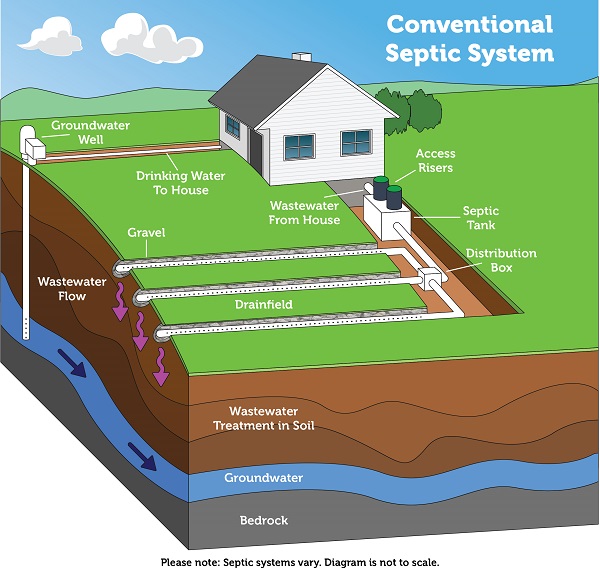
IV. Septic Tank Maintenance and Inspection in Oregon
In the state of Oregon, proper maintenance and regular inspections of septic tanks are essential to ensure the health and safety of both individuals and the environment. Here are the key regulations and responsibilities regarding septic tank maintenance and inspections in Oregon:
Regular maintenance and inspection requirements for septic tanks
1. Pumping: Septic tanks should be pumped on a regular basis to prevent the accumulation of solids and ensure proper functioning. The frequency of pumping depends on the tank size, household size, and water usage. It is recommended to consult a professional to determine the appropriate pumping schedule for your specific septic system.
2. Inspections: In Oregon, septic tanks must undergo an inspection by a licensed professional every three years. This inspection evaluates the condition of the tank, the absorption field, and checks for any signs of failure or potential issues. Regular inspections help identify problems early on and prevent costly repairs or replacements.
Responsibilities of homeowners and septic service providers
1. Homeowners: Homeowners have a responsibility to properly operate and maintain their septic tanks. This includes:
- Ensuring only appropriate waste materials are flushed or disposed of in the septic system.
- Conserving water to prevent overloading the tank.
- Regularly inspecting the tank for any signs of leaks, odors, or other issues.
- Hiring a licensed professional for pumping and inspections as required by law.
2. Septic service providers: Licensed septic service providers play a crucial role in maintaining and inspecting septic tanks. Their responsibilities include:
- Conducting thorough inspections and providing detailed reports to homeowners.
- Properly disposing of the collected waste in accordance with environmental regulations.
- Educating homeowners about proper septic system maintenance and usage.
- Performing necessary repairs or replacements when issues are detected.
Complying with these septic tank maintenance and inspection regulations in Oregon helps protect public health and the environment by preventing contamination of groundwater and surface water sources. It is important to stay informed about the specific requirements in your area and work with licensed professionals to ensure the proper functioning of your septic system.
For more detailed information on septic tank regulations in Oregon, you can refer to the Oregon Department of Environmental Quality guidelines on onsite wastewater treatment systems.

V. Environmental Impact and Water Quality Protection
As septic tanks are an essential part of many residential properties, it is crucial to understand their impact on groundwater and surface water quality. Improperly maintained or failing septic systems can contaminate water sources with harmful bacteria, viruses, and nutrients, posing a risk to both the environment and public health. To mitigate these risks, Oregon has established regulations and guidelines for the installation, maintenance, and inspection of septic tanks.
How septic tanks can impact groundwater and surface water quality
- Groundwater Contamination: When septic systems are not functioning correctly or are overwhelmed with wastewater, contaminants can seep into the surrounding soil and eventually reach the groundwater, the primary source of drinking water for many communities. This can lead to contamination of drinking water wells and result in health hazards.
- Surface Water Pollution: Septic system failures can also result in the pollution of surface water bodies such as lakes, rivers, and streams. When untreated sewage enters these water bodies, it can disrupt the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems and threaten human and animal health.
Regulations in place to protect the environment and public health
To protect water quality and prevent the contamination of groundwater and surface water, Oregon has implemented strict regulations and guidelines for septic system installation and maintenance. These regulations include:
- Oregon Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ): The DEQ is responsible for overseeing septic system regulation and compliance. They provide guidelines for system design, installation, and operation to ensure that septic tanks are properly constructed and maintained.
- On-Site Septic System Rules: Oregon has specific rules in place for the design and installation of septic systems. These rules specify setback distances from sensitive areas, such as wells, water bodies, and property lines, to minimize the risk of contamination.
- Regular Inspections: It is mandatory for septic systems to be inspected regularly to ensure their proper functioning. Inspections help identify any issues or failures early on, allowing for timely repairs and preventing potential environmental contamination.
- Proper Maintenance: Property owners are required to properly maintain their septic systems, including regular pumping and maintenance of the tanks. Regular maintenance helps prevent system failures and ensures the longevity of the septic system.
By adhering to these regulations and guidelines, individuals can contribute to the protection and preservation of Oregon’s water resources. It is also important for property owners to familiarize themselves with the specific requirements and regulations in their local jurisdiction.
For more information on septic tank regulations in Oregon, you can visit the Oregon DEQ website.

VI. Septic Tank Pumping and Disposal Requirements
In Oregon, septic tank pumping and disposal requirements are in place to ensure the proper functioning and health of septic systems. It is essential for homeowners to understand these regulations to avoid potential issues and maintain the longevity of their septic tanks. Here are some key points to know:
Frequency of septic tank pumping
Septic tanks in Oregon should be pumped every three to five years, depending on the size of the tank and the number of occupants in the household. Regular pumping is necessary to remove solid waste buildup and prevent clogs and system failure. Homeowners can consult a licensed septic contractor to determine the appropriate pumping schedule for their tank.
Guidelines for proper disposal of septic waste
When it comes to the disposal of septic waste, homeowners must follow specific guidelines to ensure environmental safety. Here are some important considerations:
- Use a licensed septic contractor: Homeowners should hire a licensed septic contractor to pump and dispose of their septic waste. These professionals have the necessary equipment and knowledge to handle and dispose of waste properly.
- Use authorized disposal facilities: Septic waste should be disposed of at authorized facilities that comply with state and local regulations. These facilities are designed to handle and treat septic waste in a way that minimizes potential environmental impacts.
- Avoid illegal dumping: It is illegal to dump septic waste in driveways, storm drains, or any area that is not specifically designated for septic waste disposal. Homeowners should always follow proper disposal procedures to prevent contamination of water sources and protect public health.
By adhering to these septic tank pumping and disposal requirements, homeowners in Oregon can maintain the effectiveness and longevity of their septic systems while also protecting the environment and public health.
For more information on septic tank regulations in Oregon, you can visit the Oregon Department of Environmental Quality’s website.

VII. Enforcement and Penalties for Non-compliance
Consequences of failing to comply with septic tank regulations
In Oregon, it is crucial to adhere to septic tank regulations to protect the environment and public health. Failing to comply with these regulations can have serious consequences, including:
- Environmental contamination: Improperly maintained or malfunctioning septic tanks can lead to the leakage of untreated wastewater into the ground, contaminating soil and groundwater sources. This pollution can harm nearby streams, lakes, and drinking water sources.
- Health risks: Untreated wastewater contains harmful bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens that can pose significant health risks to both humans and animals. Exposure to contaminated water can lead to gastrointestinal illnesses, respiratory infections, and other serious health issues.
- Legal liabilities: Non-compliance with septic tank regulations can result in legal liabilities. If the contamination from a faulty septic system causes harm to neighboring properties or individuals, the responsible party may face legal action, including lawsuits and fines.
Potential penalties and legal actions
Oregon’s regulatory authorities take septic tank violations seriously, and there are potential penalties and legal actions for non-compliance. These may include:
- Fines: Violators may be subject to fines imposed by the local health department or regulatory agency. The amount of the fine can vary depending on the severity of the violation and the jurisdiction.
- Corrective actions: In addition to fines, violators may be required to take necessary corrective actions to rectify the non-compliance. This could involve repairing or replacing the septic system, conducting inspections, or implementing ongoing maintenance measures.
- Revocation of permits: If a property owner repeatedly fails to comply with septic tank regulations, their operating permit may be revoked. This means they will no longer be authorized to operate the septic system, and alternative wastewater treatment solutions may need to be implemented.
It is essential for property owners in Oregon to educate themselves about the septic tank regulations specific to their area and ensure compliance to avoid these potential penalties and legal actions. Regular maintenance and proper usage of septic systems not only protect the environment but also safeguard the health and well-being of the community.
For more information on septic tank regulations in Oregon, please visit the Wikipedia page on septic tanks.

IX. Public Outreach and Education Initiatives
Resources available for homeowners to learn more about septic tanks
In Oregon, septic tank regulations are in place to protect public health and the environment. Homeowners who have or are planning to install a septic system need to be aware of these regulations and their responsibilities. Fortunately, there are resources available to help homeowners understand septic tank systems and ensure compliance with the regulations.
1. Oregon Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ)
The Oregon DEQ is the agency responsible for overseeing septic system regulations in the state. They provide valuable information and resources for homeowners, including guidance on septic system installation, operation, and maintenance. Their website offers downloadable guides, videos, and frequently asked questions to address common concerns and educate homeowners about septic systems.
2. Local Health Departments
Each county in Oregon has a local health department that deals with septic system permitting and inspections. These departments have knowledgeable staff who can answer questions and provide guidance regarding septic tanks. Homeowners can contact their local health department to learn about local regulations, permit requirements, and available resources.
3. Professional Septic System Contractors
Working with a professional septic system contractor is crucial for proper installation, maintenance, and repair of septic tanks. These contractors have the knowledge and experience to ensure compliance with regulations and can provide homeowners with valuable guidance and advice. It is essential to choose a licensed and reputable contractor for septic system-related work.
4. Homeowner Associations and Community Groups
Many homeowner associations and community groups in Oregon organize informational sessions and workshops on septic systems. These events provide opportunities for homeowners to learn from experts and ask questions specific to their situation. Participating in these activities can help homeowners stay informed about the latest regulations and best practices for septic systems.
5. Online Resources and Publications
There are various online resources and publications available that offer detailed information on septic systems. Homeowners can find articles, research papers, and case studies that explore various aspects of septic tank regulations and practices. These resources can provide a deeper understanding of septic systems and help homeowners make informed decisions.
It is essential for homeowners in Oregon to be proactive in educating themselves about septic tank regulations. By utilizing the available resources and staying informed, homeowners can ensure the proper operation of their septic systems and contribute to the protection of public health and the environment.
X. Comparison to other States’ Septic Tank Regulations
Brief comparison of Oregon’s septic tank regulations with regulations in neighboring states
Oregon’s septic tank regulations aim to protect public health and the environment by ensuring proper treatment of wastewater. Let’s compare Oregon’s regulations with those of its neighboring states to see how they stack up.
Oregon:
- In Oregon, septic systems require a permit from the local health department.
- Regular inspections and maintenance are required every 3 years to ensure proper functioning.
- There are specific setback requirements to prevent septic systems from being too close to wells, bodies of water, and property lines.
- Oregon has mandatory septic system inspections for property transfers or expansions.
- The state offers financial assistance programs for repairing or replacing failing septic systems.
Washington:
- In Washington, septic systems also require permits, which are issued by the local health department.
- Inspections are required every 1-3 years, depending on the system type.
- There are setback requirements to protect water sources and neighboring properties.
- Washington has mandatory septic system inspections during property transfers.
- The state offers low-income grants and loans for repairing or replacing failing septic systems.
California:
- In California, the state’s water board oversees septic system regulations.
- Permits are required from local environmental health offices.
- Inspections are required every 1-5 years, depending on the system type and location.
- There are setback requirements to protect water sources and prevent contamination.
- California has mandatory septic system inspections during property transfers.
- The state offers loan programs for low-income homeowners to repair or replace failing septic systems.
It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the specific regulations in your state and local jurisdiction to ensure compliance. Failure to comply with septic tank regulations can result in fines and potential health and environmental risks.
For more information on septic tank regulations in each state, you can visit the following links:
- Oregon septic system regulations
- Washington septic system regulations
- California septic system regulations
Remember, proper maintenance and care of your septic system are crucial for its longevity and minimizing potential risks to yourself and the environment.