I. Introduction
Why Septic Tank Requirements Are Important in Georgia
Septic tank requirements are crucial for maintaining a healthy and safe environment in Georgia. The state has specific regulations in place to ensure that septic systems function properly and do not pose any threats to public health or the environment. Here are a few reasons why septic tank requirements are important in Georgia:
1. Protection of Groundwater: Septic systems can potentially contaminate groundwater if not properly maintained. Groundwater is a vital source of drinking water for many residents in Georgia, and contamination can lead to serious health issues. Following septic tank requirements helps prevent groundwater pollution and protects public health.
2. Prevention of Soil Contamination: A malfunctioning septic system can release harmful bacteria, viruses, and other contaminants into the soil. These contaminants can seep into nearby water bodies, posing risks to aquatic life and recreational activities. Adhering to septic tank requirements helps ensure that soil is protected from contamination.
3. Avoidance of Structural Damage: Inadequate septic systems can cause structural damage to buildings and properties. Improperly treated wastewater can corrode pipes, weaken foundations, and degrade soil quality. By following septic tank requirements, homeowners can minimize the risk of expensive repairs and maintain the value of their properties.
4. Compliance with Legal Obligations: Georgia has specific laws and regulations regarding septic systems that homeowners must comply with. Failure to meet these requirements can result in legal consequences and fines. By following septic tank requirements, homeowners can avoid legal complications and ensure that their properties are in compliance with the law.
5. Protection of Public Health: Properly functioning septic systems prevent the spread of diseases and viruses that can be present in wastewater. Following septic tank requirements helps ensure that the treatment and disposal of wastewater are done correctly, reducing the risk of illness and protecting public health.
It is important for homeowners in Georgia to familiarize themselves with the septic tank requirements applicable in their area. These requirements may vary depending on factors such as property size, location, and local regulations. Consulting with a septic system professional can help ensure that your septic system meets all the necessary requirements and functions properly.
By adhering to septic tank requirements, homeowners can contribute to a cleaner environment, protect public health, and maintain the value of their properties. It is a responsibility that should not be taken lightly, as it has far-reaching effects on the well-being of both individuals and communities.

II. Georgia Department of Public Health Guidelines
Overview of the Georgia Department of Public Health Guidelines for Septic Tanks
If you live in Georgia and are planning to install a septic tank, it is important to understand the guidelines set by the Georgia Department of Public Health (DPH). These guidelines are in place to ensure proper installation and maintenance of septic systems, which are essential for the protection of public health and the environment. Here is an overview of the key guidelines set by the DPH:
1. Permitting and Inspection: Before installing a septic tank, you must obtain a permit from the DPH. The permit ensures that the installation meets the required standards. Once the installation is complete, a DPH representative will conduct an inspection to ensure compliance with the guidelines.
2. Site Evaluation: The DPH requires a site evaluation to determine the suitability of the location for a septic tank. Factors such as soil type, groundwater level, and proximity to water bodies are taken into consideration to minimize environmental impact.
3. Tank Sizing: The size of the septic tank depends on factors such as the number of bedrooms in the house and the estimated water usage. The DPH provides specific guidance on tank sizing to ensure proper wastewater treatment and prevent system overload.
4. Drainfield Design: The design of the drainfield, also known as the leach field, is crucial for the proper functioning of the septic system. The DPH guidelines provide specifications for the size and placement of the drainfield to ensure proper wastewater distribution and filtration.
5. Regular Maintenance: The DPH emphasizes the importance of regular maintenance and inspection of septic systems to prevent system failures and protect public health. It is recommended to have the septic tank pumped every 3-5 years and to have the system inspected periodically for any signs of damage or malfunction.
Key Requirements for Septic Tank Installation in Georgia
When installing a septic tank in Georgia, it is important to adhere to the following key requirements outlined by the Georgia Department of Public Health:
- Obtain a permit from the DPH before installation.
- Conduct a site evaluation to determine suitability.
- Size the septic tank according to the guidelines.
- Design the drainfield based on DPH specifications.
- Perform regular maintenance and inspection of the system.
By following these requirements, you can ensure the proper installation and functioning of your septic tank, contributing to the protection of public health and the environment in Georgia.

III. Permitting and Inspections
Process of Obtaining a Septic Tank Permit in Georgia
In Georgia, getting a permit for a septic tank is an essential step to ensure the proper installation and operation of your septic system. Here is a simplified breakdown of the process:
1. Site Evaluation: A site evaluation is the first step in determining the suitability of your property for a septic system. A qualified professional will assess the soil conditions and the size and location of your septic tank.
2. Design and Permit Application: Once the site evaluation is complete, a septic system design will be created based on the specific needs of your property. The design, along with the required documentation, will then be submitted to the local health department for review and approval.
3. Permit Approval: The local health department will review the septic system design and ensure that it complies with the state’s regulations and requirements. If approved, you will be granted the septic tank permit, allowing you to proceed with the installation.
4. Installation and Inspection: The septic system installation must be performed by a licensed contractor following the approved design. After the installation, the local health department will conduct an inspection to verify that the septic system meets all the necessary standards.
5. Final Approval: Once the inspection is passed, you will receive the final approval for your septic system. It is crucial to keep a copy of the permit for future reference.
It’s worth noting that the process may vary slightly between different counties in Georgia. It is recommended to contact your local health department for specific guidelines and requirements.
Importance of Regular Inspections and Maintenance
Regular inspections and maintenance of your septic system are crucial to ensure its proper functioning and prevent potential issues. Here are a few reasons why regular inspections are important:
1. Identifying Problems: Regular inspections can help detect any issues or potential problems with your septic system early on. This allows for prompt repairs or adjustments, preventing more significant and costly problems in the future.
2. Preventing Health Risks: A malfunctioning septic system can pose serious health risks, including contaminated groundwater and exposure to harmful bacteria. Regular inspections help maintain a safe and healthy environment for you and your family.
3. Extending Lifespan: Proper maintenance and regular inspections can extend the lifespan of your septic system. By identifying and addressing any minor issues early on, you can prevent the need for costly repairs or premature replacement.
4. Compliance with Regulations: Regular inspections ensure that your septic system remains in compliance with local health department regulations. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines and penalties.
5. Peace of Mind: Knowing that your septic system is well-maintained and functioning properly provides peace of mind. You can enjoy your home without worrying about potential septic system issues.
To ensure the longevity and efficiency of your septic system, it is recommended to schedule regular inspections and maintenance with a qualified professional. They can provide guidance on the frequency of inspections based on your system’s specific requirements.

IV. Design and Sizing Guidelines
Design Requirements for Septic Tanks in Georgia
When it comes to designing a septic tank system in Georgia, there are specific requirements that must be followed to ensure proper functionality and compliance with regulations. Here are some important design requirements to keep in mind:
1. Number of Compartments: A septic tank in Georgia must have at least two compartments. The purpose of multiple compartments is to allow for the separation of solid waste, liquids, and floating scum within the tank.
2. Tank Material: Septic tanks must be made of concrete, fiberglass, or other approved watertight materials. This is to ensure that the tank is durable, leak-proof, and able to withstand the pressure of wastewater.
3. Inlet and Outlet Placement: The inlet and outlet for the septic tank should be properly positioned to allow for efficient flow of wastewater. The inlet should be located near the top of the tank, while the outlet should be positioned near the bottom.
4. Ventilation: Proper ventilation is crucial for a septic tank system. Vent pipes should be installed to allow for the release of gases that may build up inside the tank. These vent pipes should extend to a safe distance above ground level.
5. Baffles: Baffles are devices that help to control the flow of wastewater within the tank. They should be installed in the inlet and outlet pipes to prevent the solid waste from entering the drainfield.
For detailed information on septic tank design requirements in Georgia, you can refer to the Georgia State Rules and Regulations for On-site Sewage Management.
Calculating the Proper Size for a Septic Tank
The size of a septic tank is determined by factors such as the number of bedrooms in a house, the daily water usage, and the soil conditions in the area. Here is a general guideline for calculating the proper size of a septic tank in Georgia:
1. Number of Bedrooms: The size of the septic tank is often based on the number of bedrooms in a house. For example, a two-bedroom house would typically require a 750-gallon septic tank, while a three-bedroom house would require a 1,000-gallon tank.
2. Water Usage: The daily water usage is another important factor to consider. A larger household with higher water usage may require a larger septic tank to accommodate the increased wastewater volume.
3. Soil Conditions: The type of soil in the area can also influence the size of the septic tank. Soil with poor drainage may require a larger tank to allow for more storage and treatment of wastewater.
It is important to note that these are general guidelines, and it is recommended to consult with a professional engineer or septic tank contractor to determine the specific size requirements for your property.
By following the design requirements and properly sizing the septic tank, you can ensure the efficient and effective treatment of wastewater on your property while maintaining compliance with Georgia regulations.
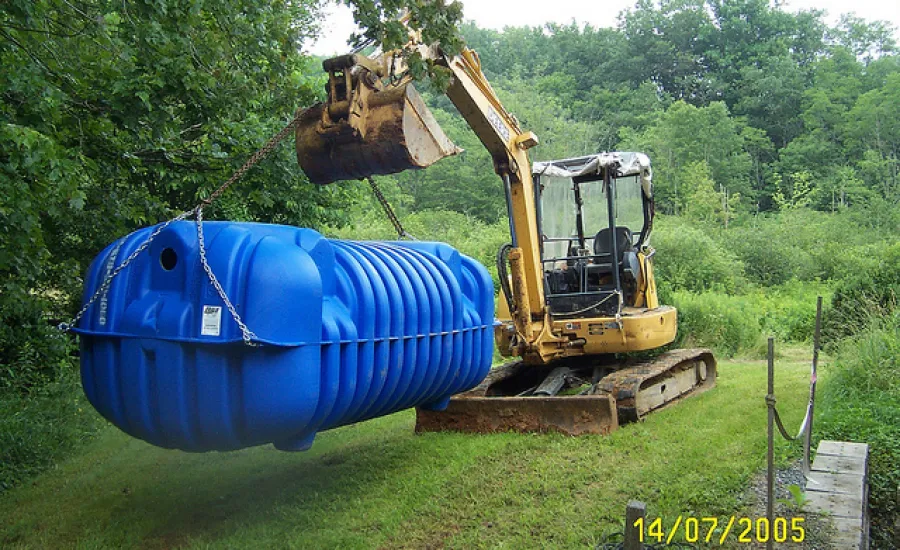 Source: transform.octanecdn.com
Source: transform.octanecdn.com
V. Drainfield Requirements
When it comes to septic systems in Georgia, proper drainfield design, installation, and maintenance are crucial. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
Key Considerations for Drainfield Design and Installation in Georgia
1. Soil Type: The type of soil on your property will impact the drainfield design. Soil with good percolation rates is ideal for efficient wastewater treatment.
2. Size and Shape: The size and shape of the drainfield will depend on the number of bedrooms in your home and the amount of wastewater generated. It needs to be properly dimensioned to ensure effective treatment.
3. Setback Requirements: Georgia has specific setback requirements that must be followed when designing and installing a drainfield. These requirements ensure that the system is located a safe distance from wells, property lines, and water bodies.
4. Slope Requirements: The drainfield should have a proper slope to allow for the natural flow of wastewater. The slope requirements in Georgia are typically between 2% and 6%.
5. Ventilation: Adequate ventilation is essential for the proper functioning of the drainfield. It helps to prevent the buildup of harmful gases and odors.
For more detailed information on drainfield requirements in Georgia, you can refer to the Wikipedia page on septic drainfields. It provides in-depth information on the various components of a drainfield and their role in wastewater treatment.
Importance of Proper Drainfield Maintenance
Proper maintenance of the drainfield is essential to ensure its longevity and prevent issues such as system failure and groundwater contamination. Here are some maintenance tips:
1. Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections of your septic system to identify any signs of potential issues early on.
2. Pumping: Regular pumping of the septic tank is necessary to remove accumulated sludge and prevent it from clogging the drainfield.
3. Water Conservation: Be mindful of water usage to prevent overloading the septic system. Fix any leaks promptly and avoid excessive water usage.
4. Proper Disposal Practices: Avoid flushing non-biodegradable items or excessive amounts of chemicals down the drains.
5. Avoid Heavy Machinery: Do not park vehicles or operate heavy machinery on top of the drainfield, as it can damage the pipes and compact the soil.
By following these maintenance practices, you can ensure the longevity and efficiency of your drainfield, minimizing the need for costly repairs or replacements.
In conclusion, understanding drainfield requirements, designing and installing the system properly, and maintaining it regularly are essential for a functional and efficient septic system in Georgia.

VI. Alternative Systems
Overview of Alternative Septic Systems Allowed in Georgia
In addition to traditional septic systems, Georgia allows for the use of alternative septic systems. These systems provide an alternative solution for properties that may not be suitable for a conventional septic system. Here are some alternative septic systems allowed in Georgia:
- Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs): ATUs use oxygen to accelerate the breakdown of organic matter in wastewater. They are commonly used in areas with high water tables or poor soil conditions.
- Drip Irrigation Systems: Drip irrigation systems distribute effluent through a network of pipes with small holes, allowing it to slowly seep into the soil. This system is ideal for properties with limited space or rocky soil.
- Mound Systems: Mound systems involve the construction of an elevated mound of soil to provide a suitable environment for wastewater treatment and disposal. These systems are commonly used in areas with a high water table or soil that is not suitable for traditional drainfields.
- Constructed Wetlands: Constructed wetlands mimic natural wetlands and use vegetation and microbial processes to treat wastewater. This system is environmentally friendly and can be aesthetically pleasing.
- Sand Filters: Sand filters are designed to remove solids and bacteria from wastewater before it is distributed into the soil. They are commonly used in areas with high water tables or poor soil conditions.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing an Alternative System
When choosing an alternative septic system in Georgia, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Site Conditions: Evaluate the soil conditions, water table level, and available space on your property to determine which alternative system is the most suitable.
- Maintenance Requirements: Different alternative systems have varying maintenance needs. Consider the level of maintenance required and whether you are willing and able to meet those requirements.
- Cost: The cost of alternative septic systems can vary significantly. Compare the upfront costs, ongoing maintenance costs, and any potential savings to determine the most cost-effective option.
- Environmental Impact: Consider the environmental impact of the alternative system and choose one that aligns with your sustainability goals.
- Local Regulations: Ensure that the chosen alternative system complies with local regulations and obtain any necessary permits or approvals.
By carefully considering these factors and working with a qualified septic system professional, you can select the right alternative septic system for your property in Georgia.

VII. Septic Tank Pumping and Cleaning
Importance of Regular Pumping and Cleaning of Septic Tanks in Georgia
Regular pumping and cleaning of septic tanks is crucial to maintain a healthy and functioning septic system. In Georgia, proper maintenance of septic tanks is not only essential for the longevity of the system but also for protecting the environment and public health. Here are a few reasons why regular pumping and cleaning are important:
- Prevent System Failures: Regular pumping removes accumulated sludge and scum from the septic tank, preventing it from overflowing or causing sewage backups in the house or yard. Neglecting regular maintenance can lead to costly repairs or even the need for a complete system replacement.
- Protect the Environment: A malfunctioning septic system can contaminate water sources, such as wells and nearby streams, rivers, or lakes. Regular pumping and cleaning help to prevent the release of harmful bacteria, viruses, and pollutants into the environment, safeguarding water quality.
- Ensure Public Health: Inadequately maintained septic systems can pose health risks to individuals and communities. Proper septic tank pumping and cleaning reduce the chances of groundwater contamination and the spread of waterborne diseases.
Recommended Frequency and Guidelines
The recommended frequency of septic tank pumping and cleaning in Georgia varies depending on several factors, including the size of the tank, the number of occupants in the household, and the type of waste being generated. As a general guideline, it is recommended to have your septic tank pumped and cleaned every three to five years.
However, it is essential to keep in mind that these are general guidelines, and the actual pumping frequency may vary. Factors such as household size, water usage, and the presence of a garbage disposal can increase the need for more frequent pumping. Consult with a licensed septic professional to determine the best pumping schedule for your specific needs.
Proper maintenance of your septic system also includes other essential practices, such as:
- Avoiding excessive water usage.
- Disposing of household waste properly.
- Regular inspection of the septic system for signs of damage or leaks.
- Using septic-safe cleaning products and avoiding the use of harsh chemicals.
By following these guidelines and scheduling regular septic tank pumping and cleaning, you can ensure the long-term functionality and efficiency of your septic system in Georgia.
For more information on septic tank requirements and maintenance guidelines in Georgia, refer to the Georgia Department of Public Health or consult with a licensed septic professional.